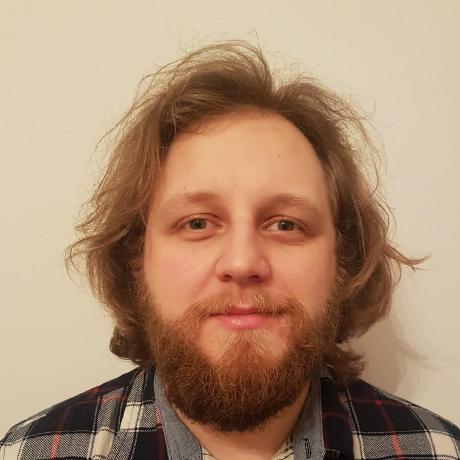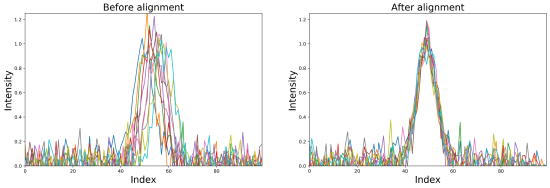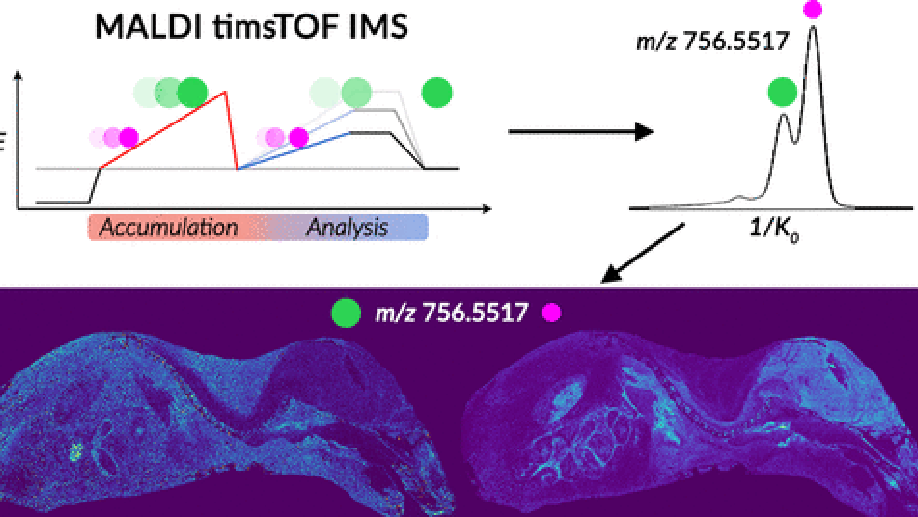
Imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) enables the spatially targeted molecular assessment of biological tissues at cellular resolutions. New developments and technologies are essential for uncovering the molecular drivers of native physiological function and disease. Instrumentation must maximize spatial resolution, throughput, sensitivity, and specificity, because tissue imaging experiments consist of thousands to millions of pixels. Here, we report the development and application of a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) trapped ion-mobility spectrometry (TIMS) imaging platform. This prototype MALDI timsTOF instrument is capable of 10 μm spatial resolutions and 20 pixels/s throughput molecular imaging. The MALDI source utilizes a Bruker SmartBeam 3-D laser system that can generate a square burn pattern of <10 × 10 μm at the sample surface. General image performance was assessed using murine kidney and brain tissues and demonstrate that high-spatial-resolution imaging data can be generated rapidly with mass measurement errors <5 ppm and ∼40 000 resolving power. Initial TIMS-based imaging experiments were performed on whole-body mouse pup tissue demonstrating the separation of closely isobaric [PC(32:0) + Na]+ and [PC(34:3) + H]+ (3 mDa mass difference) in the gas phase. We have shown that the MALDI timsTOF platform can maintain reasonable data acquisition rates (>2 pixels/s) while providing the specificity necessary to differentiate components in complex mixtures of lipid adducts. The combination of high-spatial-resolution and throughput imaging capabilities with high-performance TIMS separations provides a uniquely tunable platform to address many challenges associated with advanced molecular imaging applications.
Jeffrey M. Spraggins, Katerina V. Djambazova, Emilio S. Rivera, Lukasz G. Migas, Elizabeth K. Neumann, Arne Fuetterer, Juergen Suetering, Niels Goedecke, Alice Ly, Raf Van de Plas, Richard M. Caprioli
Analytical Chemistry,
2018
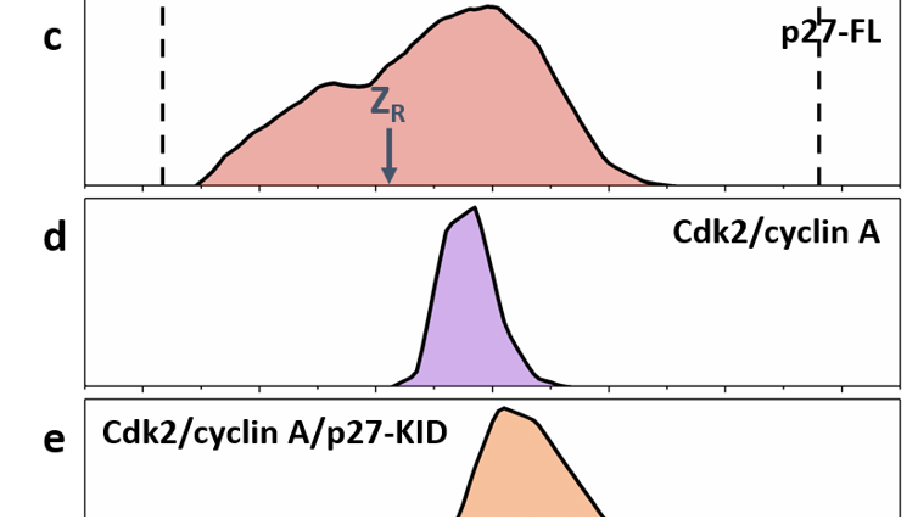
Intrinsically disordered proteins have been reported to undergo ‘disorder to order’ transitions upon binding to their partners in the cell. The extent of the ordering on binding and the lack of order prior to binding is difficult to visualize with classical structure determination methods. Binding of p27 to the Cdk2/cyclin A complex is accompanied by partial folding of p27 in the KID domain, with the retention of dynamic behaviour for function, particularly in the C-terminal half of the protein, positioning it as an exemplary system to probe conformational diversity. Here we employ native ion mobility with mass spectrometry (IM-MS) to measure the intrinsic dynamic properties of p27, both in isolation and within the trimeric complex with Cdk2/cyclin A. This stepwise approach reveals the conformational distributions of the constituent proteins and how they are restructured on complex formation; the trimeric Cdk2/cyclin A/p27-KID complex possesses significant structural heterogeneity cf. Cdk2/cyclin A. These findings support the formation of a fuzzy complex in which both the N and C termini of p27 interact with Cdk2/cyclin A in multiple closely associated states.
Rebecca Beveridge, Lukasz G. Migas, Richard Kriwacki, Perdita E. Barran
Angewandte Chemie,
2018
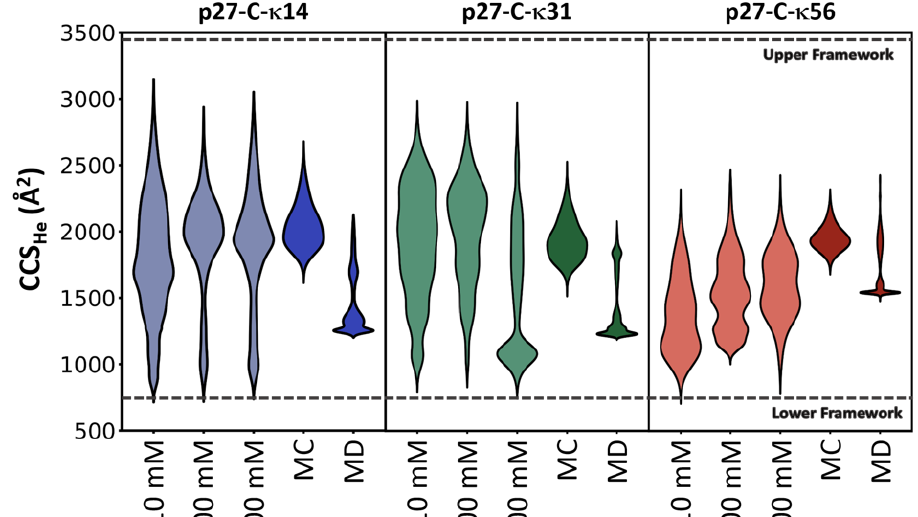
The global dimensions and amplitudes of conformational fluctuations of intrinsically disordered proteins are governed, in part, by the linear segregation versus clustering of oppositely charged residues within the primary sequence. Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry (IM-MS) affords unique advantages for probing the conformational consequences of the linear patterning of oppositely charged residues because it measures and separates proteins electrosprayed from solution on the basis of charge and shape. Here, we use IM-MS to measure the conformational consequences of charge patterning on the C-terminal intrinsically disordered region (p27 IDR) of the cell cycle inhibitory protein p27Kip1. We report the range of charge states and accompanying collisional cross section distributions for wild-type p27 IDR and two variants with identical amino acid compositions, κ14 and κ56, distinguished by the extent of linear mixing versus segregation of oppositely charged residues. Wild-type p27 IDR (κ31) and κ14 where the oppositely charged residues are more evenly distributed, exhibit a broad distribution of charge states. This is concordant with high degrees of conformational heterogeneity in solution. By contrast, κ56 with linear segregation of oppositely charged residues, leads to limited conformational heterogeneity and a narrow distribution of charged states. Molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that the interplay between chain solvation and intra-chain interactions (self-solvation) leads to conformational distributions that are modulated by salt concentration, with the wild-type sequence showing the most sensitivity to changes in salt concentration. These results suggest that the charge patterning within the wild-type p27 IDR may be optimized to sample both highly solvated and self-solvated conformational states.
Rebecca Beveridge, Lukasz G. Migas, Rahul Das, Rohit Pappu, Richard Kriwacki, Perdita E. Barran
Journal of Americal Chemical Society,
2018